The Cascading OKRs Model is a traditional, hierarchical approach where objectives set at the top level are broken down into smaller, more specific goals at each subsequent level of the organization. This method ensures that every team and individual’s work directly contributes to the company’s overarching mission.
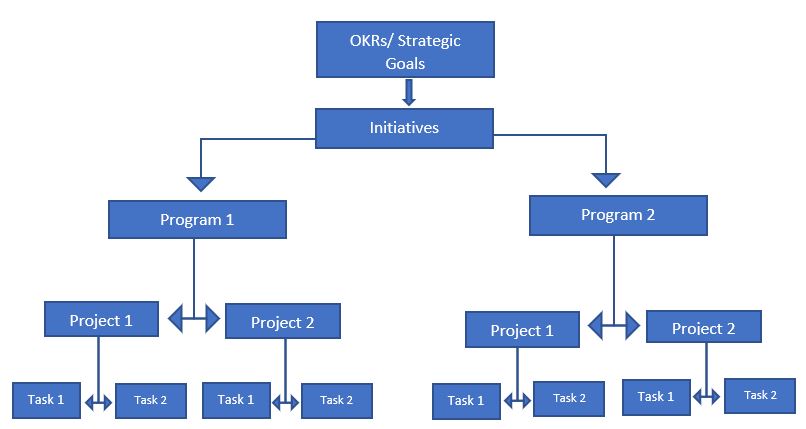
The Stages of Cascading OKRs are explained with examples:
Top-Level Objective (Company-Wide)
☑ Objective: Increase Market Share in the SaaS Industry
☑ Key Results:
1. Achieve a 20% increase in customer acquisition.
2. Expand into two new geographical markets.
3. Launch three new product features tailored for enterprise clients.
Stage 1: Cascading to the Sales Department
☑ Objective: Achieve a 20% Increase in Customer Acquisition (derived from the company KR)
☑ Key Results:
1. Close deals with 50 new enterprise customers.
2. Increase the average deal size by 15%.
3. Improve the sales conversion rate by 10%.
Stage 2: Cascading to the Regional Sales Teams
☑ Objective: Close Deals with 50 New Enterprise Customers (derived from the Sales Department KR)
☑ Key Results:
1. Generate 200 qualified leads in the new geographical markets.
2. Increase outreach efforts by 25% in target industries.
3. Achieve a 30% demo-to-deal conversion rate.
Stage 3: Cascading to the Individual Sales Team Member
☑ Objective: Generate 200 Qualified Leads in the New Geographical Markets (derived from the Regional Sales Teams KR)
☑ Key Results:
1. Reach out to 500 potential clients through targeted emails and calls.
2. Schedule 40 product demos with qualified prospects.
3. Convert 15% of demos into signed contracts (i.e., close 30 deals).
In the screenshot above, we show how Nimble’s OKR solution accomplishes this top down approach from company level to individual level .
Advantages of Cascading OKRs:
☑ Enhanced Accountability:Clarifies responsibility at every level, making it easier to track contributions and measure progress.
☑ Global Consistency for bigger corporations: Enables bigger corporations to align objectives across different regions and cultures, ensuring that global strategies are consistently implemented.
Disadvantages of Cascading OKRs:
While cascading OKRs offer significant benefits, they also come with challenges, as highlighted in John Doerr’s book Measure What Matters:
☑ Lack of Agility: The top-down structure can make it difficult for organizations to quickly adapt to changes, leading to potential stagnation in dynamic environments.
☑ Overemphasis on Hierarchy: This approach can result in a disconnect between employees and the company’s strategic goals, particularly if lower-level objectives are seen as less significant.
The Aligning OKRs Model: A Collaborative and Flexible Approach
In contrast, the Aligning OKRs Model is more flexible and collaborative. Rather than a strict top-down process, this approach encourages teams and individuals to set their own OKRs in alignment with the organization’s strategic goals, fostering a culture of collaboration and adaptability.
The Concept Behind Aligning OKRs:
☑ Strategic Goal Setting: Leadership sets broad strategic goals that guide the organization’s direction.
Example: A technology company aims to become the market leader in AI-driven solutions within the next three years. The strategic goal is: “Achieve a 25% market share in AI-driven solutions by the end of 2026.”
☑ Team-Level Alignment: Teams create OKRs that align with the organization’s strategic goals.
Example: The AI product development team sets an OKR: “Launch three new AI-driven products by Q4 2024 with an average customer satisfaction score of 90%.” This OKR directly supports the strategic goal of increasing market share by introducing innovative products.
☑ Individual Contribution: Employees set personal OKRs that contribute to their team’s objectives.
Example: A product manager within the AI team sets an OKR: “Complete the product roadmap for the first AI-driven product by Q1 2024 and ensure 100% alignment with customer needs through beta testing feedback.” This personal OKR contributes to the team’s goal of launching new products.
☑ Continuous Coordination: Regular check-ins and updates ensure that everyone remains aligned with the strategic goals.
Example: Monthly check-ins are held where the leadership reviews the progress of strategic goals, teams present updates on their OKRs, and individuals discuss challenges and achievements.
In the screenshot above, we show how Nimble’s OKR solution accomplishes the alignment of OKRs.
Advantages of Aligning OKRs:
☑ Enhanced Flexibility: Allows for adjustments as teams and individuals adapt to changes.
☑ Collaborative Culture: Encourages a culture of shared ownership, leading to higher engagement and innovation.
☑ Dynamic Goal Setting: Supports a more responsive approach to achieving objectives.
Conclusion
Aligning OKRs offers a more dynamic and collaborative approach compared to cascading OKRs. While cascading OKRs flow top-down, often leading to rigid hierarchies and potential misalignment across levels, Aligning OKRs fosters a more integrated and adaptable environment. Alignment ensures that strategic goals, team objectives, and individual contributions are interconnected and mutually reinforcing. Nimble OKR makes this seamless by providing a user-friendly platform that helps you set, track, and achieve your objectives with clarity and precision. Signup for a Free trial