I started my career in a consulting company where I was involved in a couple of truly complex projects – one, to build a custom project management system for one of the largest construction companies in India, and the second – to help the country’s top 5 Property and Casualty insurance companies procure new Unix based computer systems to run their business, following a mandate by the Indian government to all public sections organizations to do so.
Needless to say, they were both extremely complex projects – and also very different from each other. The first required an in-depth understanding of the different types of construction projects this company did – a dam/ hydroelectric power plant project was very different from an engineering plant set up projects – which was very different from a massive rail and road bridge construction project. The second required an understanding of government and public sector procurement process, benchmarking hardware and software systems and working with myriad vendors and computer system standards at a time, when no such systems or standards had ever existed.
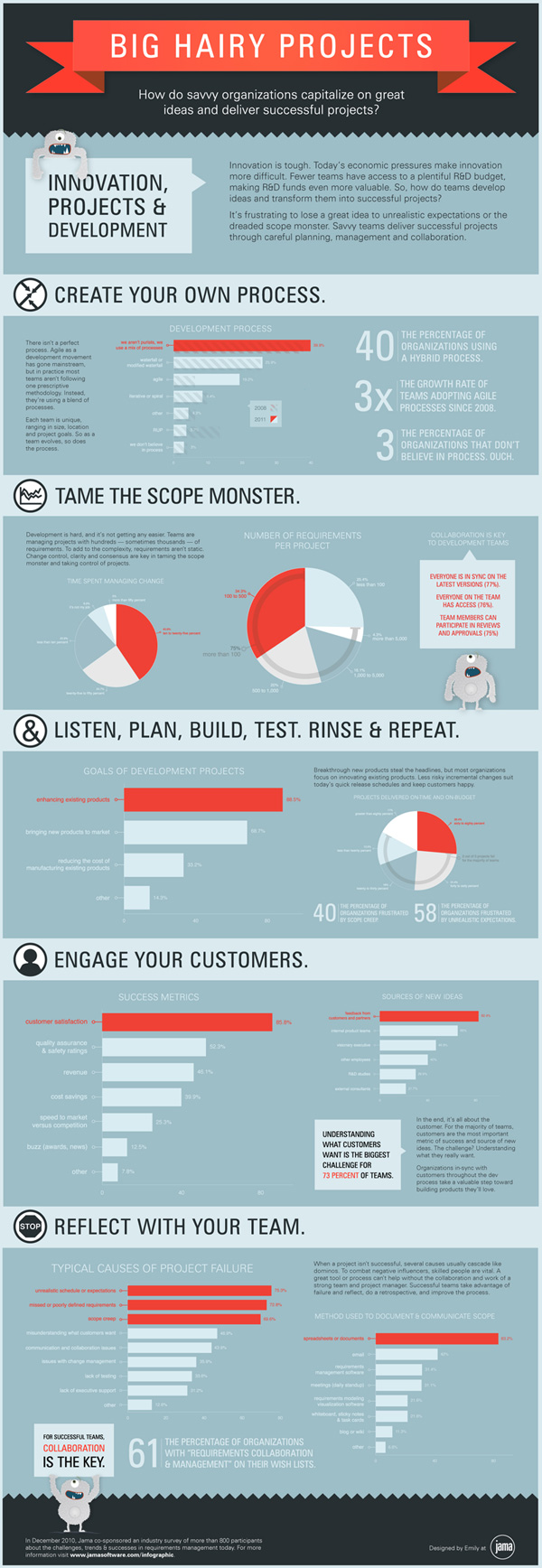
Jama Software’s study reveals that 75% of project managers handle projects comprising a minimum of 100 requirements, with one in five managing projects exceeding 1,000 requirements. These statistics underscore the scale and complexity of modern projects. Below is a summary of their additional findings:
Source: Jama Software
I didn’t know of the term then – but these were BHCPs – Bigg, Hairy, Complex Projects! – that I was fortunate enough to be part of. I learned a lot, my company learned a lot. Without going into a lot of detail, I can tell you that we struggled with the first project for a very long time, before delivering something of value which was very different from what the client and we expected at the start of the projects. We successfully helped the insurance companies place orders with the winning bidders of those Unix systems, based on technical, commercial and support benchmarks and guidelines we helped define.
Big, hairy, complex projects (BHCPs) present formidable challenges for organizations across various industries. These endeavors are characterized by their sheer scale, intricate nature, and high levels of uncertainty. Successfully navigating BHCPs requires a combination of strategic planning, effective leadership, and robust project management practices. In this article, we explore the characteristics of BHCP projects, examine typical types and famous examples, discuss strategies for organizing and managing BHCP projects, assess the applicability of Agile or Hybrid Agile methods, and provide tips for successful delivery.
So, what are BHCP Projects?
BHCP projects are – by definition – big and complex. But other aspects are hairy and difficult as well. Big, hairy, complex projects share several defining characteristics:
• Scale or size: BHCPs are often large in scope, involving extensive resources, multiple stakeholders, and significant financial investments.
• Complexity: These projects are intricate, encompassing various technical, organizational, and environmental factors that require careful coordination and management.
• Uncertainty: BHCPs face high levels of uncertainty, stemming from factors such as technological innovation, regulatory changes, and market dynamics.
• Interdependencies: There are numerous interdependencies between different components or phases of BHCPs, requiring close coordination to avoid delays or disruptions.
• Long Duration: BHCPs typically have extended timelines, spanning several years or even decades, which necessitate sustained effort and resource allocation.
• Strategic Importance: These projects are aligned with an organization’s strategic objectives and often represent significant opportunities or threats to its long-term success.
Typical Types of BHCP Projects
We all have a general understanding of big, complex projects. We see many of them – and be impacted by – in our daily lives. Several types of projects are commonly classified as BHCPs, including:
• Infrastructure Projects: Examples include the construction of highways, bridges, airports, and high-speed rail networks like the California High-Speed Rail project, a constant source of frustration where I live.
• Large-Scale IT Implementations: Enterprise-wide IT projects such as ERP system implementations or complex software development initiatives.
• Construction Mega-Projects: Projects involving skyscrapers, stadiums, or major urban development initiatives.
• Defense and Aerospace Projects: Development of military aircraft, spacecraft, or missile defense systems.
• Energy Projects: Construction of power plants, offshore wind farms, or oil and gas pipelines.
• Healthcare Infrastructure Projects: Building hospitals, medical research facilities, or implementing large-scale healthcare IT systems.
Organizing and Managing BHCP Projects
Organizing and managing BHCP projects is no trivial task. On the one hand, they require a supporting environment, where stakeholders, customers, and the project team and leadership understand the situation and are committed to provide all the support needed to make these projects successful.
Source: Research Gate
On top of that, they require a project management structure designed to handle the various moving parts of such large and complex projects, with a project leader who can manage this senior project management team. We have all heard of legendary project leaders who, with a combination of personal charisma and motivation, experience and skills, as well as strong people motivation and management skills who have won the day for their organizations.
Once such a project management team is ready, they then need to do everything to successfully plan and execute a BHCP! It requires careful planning and coordination, both from a plan and people perspective:
• Develop a Clear Project Vision and Objectives: Ensure all stakeholders understand the overarching goals and objectives of the project.
• Establish Strong Governance Structures: Implement robust governance mechanisms to provide oversight, decision-making authority, and accountability.
• Break Down the Project into Manageable Phases: Divide the project into smaller, more manageable phases or modules to facilitate better control and monitoring.
• Manage Stakeholder Expectations: Identify and engage key stakeholders early to understand their needs, concerns, and expectations.
• Allocate Resources Strategically: Allocate resources based on project priorities, critical path activities, and resource constraints.
• Build a Skilled Project Team: Assemble a diverse and skilled project team capable of addressing the multidisciplinary challenges of BHCPs.
• Foster Effective Communication: Establish clear communication channels and protocols to facilitate timely and transparent communication among project team members and stakeholders.
Plan for an effective Project Management solution that can handle all the aspects of planning and managing the project, the people and all other resources, so that all project status information, documents and reports can be effectively managed. Most of the time, a single product may not be enough to meet all the needs of such projects – and one of the key starting points for such projects would be to put together their project management solution first.
Are Agile or Hybrid Agile Methods Applicable for BHCP Projects?
Given the sheer scale and size of BHCP projects, it is very likely that at least some – if not all – parts of the projects can benefit from the use of Agile principles. For example, the technology components of a BHCP project could easily use Agile or Hybrid Agile principles. Even non-technology could be broken down into smaller portions, where at the end of each portion (sub-phase), stakeholders and customers might have a chance to review and give feedback.
Hybrid Agile Project Flow
Agile or Hybrid Agile methods and best practices/ ceremonies can be adapted and applied effectively to BHCP projects, providing flexibility, collaboration, and incremental progress:
• Flexibility: Agile methodologies allow teams to adapt to changing requirements, priorities, and market conditions more effectively.
• Iterative Development: Adopting an iterative approach enables teams to deliver value incrementally, reducing the risk of large-scale project failures.
• Team Ceremonies: Agile team ceremonies such as Daily Standups, Sprint (or sub-Phase) Retrospectives and other regular team/ customer/ stakeholder interactions can provide some of the same benefits that Agile projects have been able to achieve.
• Stakeholder Engagement: Agile methods promote continuous stakeholder engagement and feedback, ensuring alignment with stakeholder needs and expectations.
• Hybrid Approach: Combining Agile delivery/ execution principles with traditional project planning and management methodologies allows organizations to tailor their approach to the specific needs and characteristics of BHCPs.
Given the nature of BHCP projects, where value delivery may take months or even years, increasing the risks of project failure, we can argue that using an Agile or Hybrid Agile is in fact critical to running BHCP projects and dramatically improving the chances of making them successful.
Critical Success Factors for BHCP Projects
To enhance the likelihood of success in delivering BHCP projects, consider the following tips:
• Develop a comprehensive project plan that outlines clear objectives, milestones, and deliverables.
• Establish strong governance structures to provide oversight, decision-making authority, and accountability. While typical smaller projects might be run by a single or a small team of PMs, BHCP projects require experience, diversity of ideas and solutions, and the ability to build consensus.
• Foster a culture of collaboration, transparency, and continuous improvement within the project team.
• Embrace innovation and adaptability, seeking out opportunities for process improvements and technological advancements.
• Prioritize stakeholder engagement and communication throughout the project lifecycle, ensuring alignment with stakeholder needs and expectations.
• Monitor project progress closely, identifying risks and issues early and implementing mitigation strategies as needed.
• Celebrate achievements and milestones to maintain morale and motivation within the project team.
• Conduct thorough post-project reviews to capture lessons learned and identify areas for improvement in future projects.
Summary
Managing big, hairy, complex projects requires a strategic approach and a combination of effective leadership, robust project management practices, and adaptability to navigate the inherent challenges. By understanding the characteristics of BHCPs, organizing projects effectively, leveraging Agile or Hybrid Agile methodologies, and following best practices for successful delivery, organizations can enhance their ability to achieve successful outcomes in even the most complex endeavors.