What does it take to be a truly exceptional project manager today? How can you navigate the complexities of modern project landscapes while balancing human dynamics, technological advancements, and strategic foresight? As the role of a project manager evolves, so too must our understanding of the essential skills required for success.
Gone are the days when a rigid set of technical competencies sufficed. Imagine a project manager as a master conductor, orchestrating a complex interplay of human emotions, market rhythms, and technical prowess. These skills aren’t mere checkboxes on a resume but the living essence of project alchemy – the ability to turn potential into golden outcomes.
Consider the project manager who seamlessly communicates with both C-suite executives and Gen Z developers, or the one who uses behavioral economics to nudge teams toward peak performance. These multidimensional skills distinguish the good from the truly transformative in project management.
As we delve into this exploration, we challenge you to look beyond the obvious. The skills discussed here are the lenses through which successful project managers view the world, unlocking innovation, fostering resilience, and navigating modern project complexities. Whether you’re a seasoned PMO or an aspiring project manager, this article sheds light on important skills.
In today’s intensely competitive landscape, businesses face the challenge of delivering intricate projects, leading to a surge in demand for adept project managers. According to the job posting analysis done by Northeastern University, the number of project management positions is expected to rise by 11% by 2033. Despite this increasing demand, many organizations struggle with a shortage of talent, putting them at considerable risk. Hence it is of utmost importance that Project Managers evolve with the changing landscape of Project Management and specifically focus on the skills that are discussed in this article to be armored with the right skills for all the career opportunities.
Source: Northeastern.edu
1. The Evolving Landscape of Project Management
The project management space is shifting beneath our feet, transforming at a pace that would have been unimaginable just a decade ago. To truly grasp the skills required in this new era, we must first understand the seismic changes reshaping our field.
The Dissolution of Boundaries
Traditional project management operated within clearly defined parameters – scope, time, and budget formed the iron triangle that constrained and guided our efforts. Today, these boundaries are blurring, giving way to a more fluid, adaptable approach.
From Silos to Ecosystems
Projects no longer exist in isolation. They are intricate parts of larger ecosystems, interconnected with organizational strategies, market dynamics, and global trends. The modern project manager must possess the ability to see beyond the immediate project scope, understanding how each decision ripples through this vast, interconnected web.
The Rise of Cognitive Diversity
In an age where artificial intelligence can crunch numbers and generate Gantt charts, the true value of a project manager lies in their ability to harness the power of cognitive diversity.
Neurodivergent Thinking as a Superpower
Forward-thinking organizations are recognizing that neurodivergent individuals bring unique perspectives and problem-solving approaches to project teams. The ability to create an environment where these diverse thinking patterns can flourish is becoming a crucial skill for project leaders.
The Quantum Nature of Project Outcomes
The binary notion of project success or failure is giving way to a more nuanced understanding. Like Schrödinger’s cat, project outcomes exist in a superposition of states until they are observed and measured.
Embracing Ambiguity
Project managers must develop a comfort with ambiguity, understanding that in complex systems, outcomes are often probabilistic rather than deterministic. This shift requires a fundamental rewiring of how we approach risk, planning, and stakeholder management.
The Ethical Dimension of Project Management
As projects increasingly impact societal and environmental spheres, ethical considerations are moving from the periphery to the core of project management.
Moral Algebra in Decision-Making
Project managers are now called upon to perform complex moral calculations, weighing not just financial and temporal costs, but also social impact, environmental footprint, and long-term consequences of their decisions.
The Convergence of Human and Machine Intelligence
The future of project management lies not in human versus machine, but in human plus machine.
Augmented Project Intelligence
Successful project managers will be those who can seamlessly integrate AI and machine learning into their workflows, using these tools to enhance human creativity and decision-making rather than replace them.
The Gig Economy and Project Staffing
The rise of the gig economy is revolutionizing how projects are staffed and managed.
Fluid Team Dynamics
Project managers must develop skills in rapidly assembling and disassembling teams, creating cohesion and trust in short time frames, and managing a workforce that may be spread across the globe and working asynchronously.
In this evolving landscape, the project manager becomes less of a taskmaster and more of a context creator – someone who shapes the environment in which diverse teams can thrive, innovation can flourish, and complex problems can be solved.
The skills required in this new world order go beyond the technical and even beyond the traditionally recognized soft skills. They encompass a new breed of meta-skills – the ability to learn, unlearn, and relearn at pace; the capacity to synthesize vast amounts of information into coherent strategies; and the agility to pivot not just projects, but entire mindsets as circumstances demand.
As we delve deeper into the specific skills in the following sections, keep in mind this shifting landscape. The most valuable skills are those that allow us to not just navigate this new terrain, but to actively shape it, creating value in ways we’re only beginning to imagine.
2. Soft Skills in Project Management
The realm of soft skills in project management is akin to the dark matter of the universe – invisible yet exerting a powerful influence on everything around it. These skills, often underestimated, are the true differentiators in today’s complex project environments.
1. Communication: The Neural Network of Projects
Communication in project management has evolved far beyond status reports and team meetings. It’s now a multidimensional skill that requires:
- Neuroplasticity in communication styles: Adapting not just to different stakeholders, but to the evolving communication preferences within a single project lifecycle.
- Mastery of subtext and metacommunication: Understanding the unspoken currents that flow beneath the surface of team interactions.
- Quantum communication: The ability to convey complex ideas simply, and simple ideas profoundly.
2. Leadership: Conducting the Symphony of Talent
Leadership in the new age of project management is less about command and control, and more about:
- Catalytic leadership: Initiating reactions and then stepping back to let the team’s chemistry take over.
- Fractal leadership: Demonstrating leadership principles that can be replicated at every level of the project hierarchy.
- Servant leadership 2.0: Going beyond serving the team to serving the larger purpose of the project and its impact on the world.
3. Emotional Intelligence: The Project’s Limbic System
Emotional intelligence in project management has deepened to include:
- Emotional forecasting: Predicting and preparing for the emotional journey of the team throughout the project lifecycle.
- Empathy mapping: Creating detailed empathy maps for stakeholders to anticipate needs and concerns before they arise.
- Emotional contagion management: Skillfully modulating the emotional tone of the project to maintain optimum team performance.
4. Adaptability: The Evolutionary Advantage
Adaptability has become less about reacting to change and more about:
- Proactive morphing: Reshaping the project approach in anticipation of changes, not just in response to them.
- Cognitive flexibility: The ability to switch between different thinking modes – analytical, creative, strategic – as the situation demands.
- Comfort with discomfort: Cultivating a team culture that thrives on change rather than merely tolerating it.
5. Conflict Resolution: Turning Disagreements into New Ideas
Modern conflict resolution in project management involves:
- Conflict as a catalyst: Viewing disagreements as opportunities for breakthrough thinking rather than obstacles.
- Differential diagnosis of conflict: Distinguishing between conflicts that stem from misalignment of goals, methods, or values.
- Conflict ecosystem management: Understanding and managing the ripple effects of conflicts across the entire project ecosystem.
3. Hard Skills in Project Management
While soft skills provide the framework, hard skills are the tools that shape project outcomes. These skills are evolving rapidly, influenced by technological advancements and changing business paradigms.
6. Technical Proficiency: Beyond the Basics
Technical proficiency now encompasses:
- Polyglot project management: Fluency in multiple project management methodologies, able to code-switch between Agile, Waterfall, and hybrid approaches seamlessly.
- Technological synesthesia: The ability to see connections between disparate technologies and leverage them for project success.
- Digital twin mastery: Using digital twin technology to simulate and optimize project processes before implementation.
7. Risk Management: From Mitigation to Exploitation
Risk management has evolved to include:
- Opportunity in risk: Identifying how risks can be transformed into competitive advantages.
- Complexity theory in risk assessment: Understanding how small risks can cascade into significant impacts in complex systems.
- Predictive risk analytics: Leveraging big data and AI to forecast potential risks before they materialize.
8. Budgeting and Cost Control: Financial Alchemy
Modern budgeting and cost control involve:
- Value stream mapping: Identifying and optimizing the flow of value through the entire project lifecycle.
- Dynamic resource allocation: Real-time adjustment of resources based on AI-driven project performance data.
- Blockchain for project finance: Utilizing blockchain technology for transparent, efficient financial tracking and reporting.
9. Scheduling and Time Management: Chronos and Kairos
Advanced scheduling and time management now include:
- Quantum scheduling: Applying principles of quantum mechanics to project scheduling, allowing for multiple timeline scenarios.
- Chronobiology in project planning: Aligning project phases with team members’ natural biological rhythms for optimal performance.
- Time-boxing 2.0: Using AI to dynamically adjust time-boxes based on real-time productivity data and project needs.
10. Quality Management: From Control to Creation
Quality management has shifted focus:
- Quality by design: Embedding quality considerations into every decision point of the project.
- Biomimicry in quality processes: Learning from nature’s time-tested quality assurance methods.
- Quantum quality metrics: Developing metrics that capture both the tangible and intangible aspects of project quality.
4. Specialized Skills for Different Project Management Roles
As projects become more complex and specialized, so do the roles within project management. Each role requires a unique blend of skills tailored to its specific challenges and responsibilities.
11. Project Coordinator Skills
Project coordinators are the synapses of the project nervous system, requiring skills in:
- Micro-coordination: Managing the minute details that can make or break a project’s smooth operation.
- Information ecology: Creating and maintaining a healthy flow of information throughout the project ecosystem.
- Adaptive documentation: Developing living documents that evolve with the project, rather than static reports.
12. Project Manager Skills
Project managers must be polymaths, blending:
- Strategic empathy: The ability to align project goals with the emotional and professional needs of team members and stakeholders.
- Complexity navigation: Guiding projects through increasing levels of complexity and ambiguity.
- Futures thinking: Anticipating how current project decisions will shape future possibilities and constraints.
13. Program Manager Skills
Program managers operate at a meta-level, requiring:
- Systems orchestration: Harmonizing multiple projects into a coherent, value-driving program.
- Strategic plasticity: The ability to reshape program strategy in response to changing organizational needs and market conditions.
- Cross-pollination facilitation: Enabling the transfer of insights and innovations between projects within the program.
14. Portfolio Manager Skills
Portfolio managers need to think at the ecosystem level, focusing on:
- Portfolio synergy creation: Identifying and fostering synergies between different projects and programs.
- Organizational futurism: Aligning the project portfolio with the organization’s long-term vision and potential future scenarios.
- Value constellation mapping: Understanding how different projects contribute to the overall value proposition of the organization.
These specialized roles form a symbiotic network within the project management field. The most successful organizations recognize that while each role has its distinct skill set, there needs to be a shared foundation of adaptability, systems thinking, and ethical consideration.
15. Leverage Your Project Management Expertise with Cutting-Edge Tools
Having grasped the essential skills for excelling in project management, it’s crucial to arm yourself with state-of-the-art project management tools. Nimble, designed to streamline and enhance project managers’ workflows. Nimble’s key offerings include:
All-in-one Adaptive Project Management: A comprehensive solution that adapts to your unique project needs, providing you with the flexibility to manage projects efficiently.
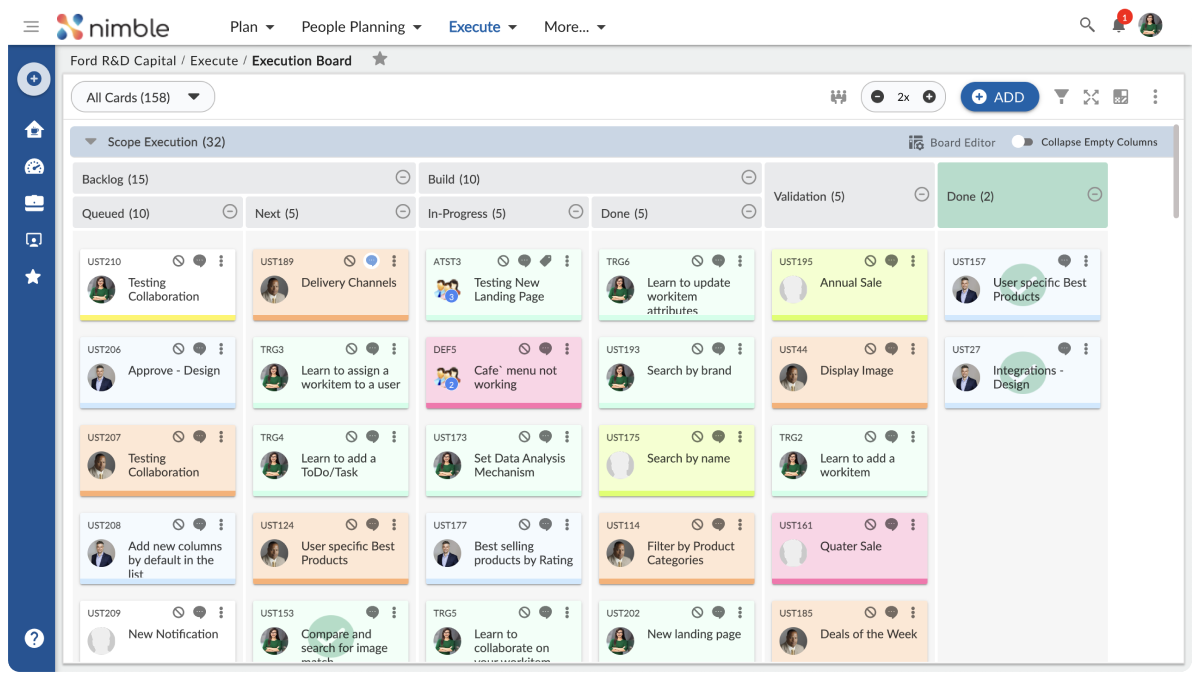
Comprehensive Visual Work Management: Facilitates successful team collaboration and seamless project delivery, whether you’re handling projects or routine tasks. Nimble supports both traditional tools, such as Gantt charts and task lists, and Agile tools, like Kanban boards.
Check out Nimble! Sign up for a Free Trial
Conclusion
As we move forward, the boundaries between these roles may blur, with project professionals needing to flex between different skill sets as the situation demands. The key to success in this evolving landscape is not just mastering a specific set of skills, but developing the meta-skill of skill acquisition itself – the ability to rapidly learn, apply, and innovate new approaches as the project environment continues to evolve.
In closing, remember that mastering these skills is an ongoing journey, one that requires continuous learning, adaptability, and courage. As you integrate these skills into your practice, you’ll create a unique approach that resonates with your projects, teams, and vision of success. Armed with this comprehensive skill set, you’re not just managing projects – you’re shaping the future itself, turning bold visions into tangible realities, one project at a time.
The future of project management is bright, dynamic, and full of potential. Embrace these skills, and lead the way in this exciting new era of project management excellence.