Project management has undergone a significant transformation over the past few decades, driven by technological advancements, evolving methodologies, and shifting workplace dynamics. The traditional, rigid frameworks have given way to more flexible, adaptive, and collaborative approaches. This article delves into the key differences between project management today and in the past, highlighting the impact of technology, methodologies, team dynamics, and the growing emphasis on soft skills and sustainability.
Technological Advancements
One of the most significant changes in project management is the advent of technology. In the past, project managers relied heavily on manual processes and physical documentation. Tools such as Gantt charts were drawn by hand or created using basic software. Communication was primarily face-to-face or via telephone, with emails and basic file-sharing systems representing the cutting edge of technology.
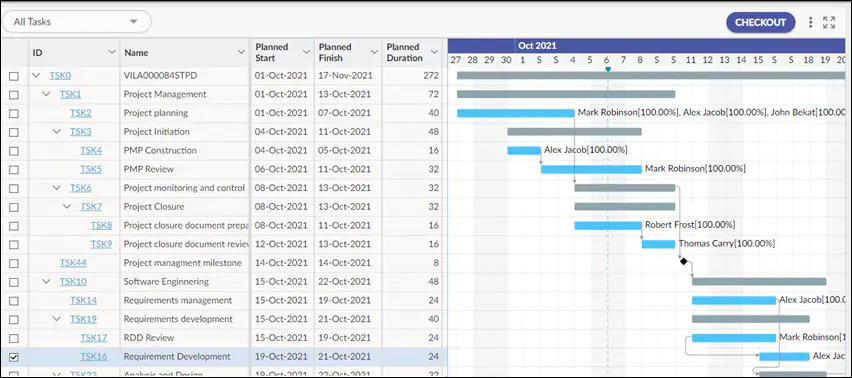
Nimble Gantt chart view
Today, technology has revolutionized project management. Modern project management software like Nimble offer comprehensive platforms for planning, executing, and monitoring projects. These tools facilitate real-time collaboration, task assignment, progress tracking, and reporting. Cloud computing has further enhanced these capabilities, allowing team members to access project information from anywhere in the world, fostering a more global and remote workforce.
Moreover, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are beginning to play significant roles in project management. AI can predict project risks, optimize resource allocation, and automate routine tasks, enabling project managers to focus on strategic decision-making. Advanced data analytics provide insights into project performance, helping managers make data-driven decisions and improve future project outcomes.
Methodological Shifts
Project management methodologies have also evolved significantly. Historically, the Waterfall model was the predominant approach. This linear, sequential method involves distinct phases, such as initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure. Each phase must be completed before the next begins, making the process inflexible and challenging to adapt to changes.
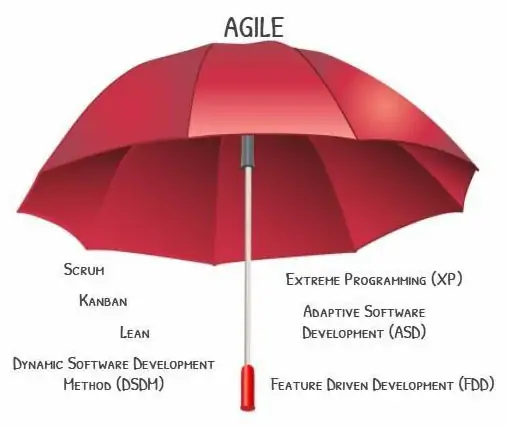
In contrast, today’s project management favors more flexible methodologies like Agile, Scrum, and Kanban. Agile, for instance, emphasizes iterative development, where projects are broken into smaller, manageable increments called sprints. This approach allows teams to respond to changes quickly, incorporating feedback and adjusting plans as needed. Scrum, a subset of Agile, introduces roles such as Scrum Master and Product Owner, and ceremonies like daily stand-ups and sprint reviews, to foster collaboration and continuous improvement.
Kanban, another modern methodology, focuses on visualizing work, limiting work in progress, and optimizing flow. It uses boards and cards to represent tasks, making it easy to see the status of work at a glance. These methodologies promote a culture of adaptability, continuous learning, and customer-centricity, which contrasts sharply with the rigid, plan-driven Waterfall approach.
Team Dynamics and Remote Work
The composition and dynamics of project teams have also transformed. In the past, project teams were typically co-located, working in the same physical space. Communication was predominantly in-person, with meetings held in conference rooms and progress tracked on physical boards or charts.
The rise of digital tools and remote work has changed this dynamic. Today’s project teams are often geographically dispersed, working across different time zones and cultures. Communication tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom have become essential, enabling seamless virtual meetings, instant messaging, and file sharing. These tools support asynchronous communication, allowing team members to collaborate effectively despite differences in their working hours.
Remote work has also necessitated a shift in management styles. Traditional command-and-control approaches are less effective in a remote environment. Instead, project managers now focus on building trust, empowering team members, and fostering a culture of accountability and autonomy. This shift has led to increased emphasis on soft skills, such as communication, emotional intelligence, and conflict resolution.
Emphasis on Soft Skills and Customer-Centricity
In the past, project management was often seen as a purely technical role, focused on planning, scheduling, and controlling. However, the modern project management landscape recognizes the importance of soft skills and customer-centricity in achieving project success.
Effective communication, leadership, teamwork, and stakeholder management are now considered crucial competencies for project managers. They must navigate complex stakeholder landscapes, managing expectations and fostering relationships with clients, team members, and other stakeholders. This requires a high degree of emotional intelligence, the ability to understand and manage one’s emotions and those of others, as well as conflict resolution and negotiation skills.
Moreover, project managers must adopt a customer-centric mindset, ensuring that projects are aligned with customer needs and expectations. This involves gathering customer feedback, incorporating their input into project plans, and delivering outcomes that create value and meet customer requirements.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
Modern project management also places a greater emphasis on sustainability and ethical considerations. In the past, the primary focus was often on delivering projects on time, within scope, and on budget. While these factors remain important, there is now a growing recognition of the need to consider the broader impact of projects on society and the environment.
Sustainable project management involves integrating environmental, social, and economic considerations into project planning and execution. This might include reducing waste, using resources efficiently, and ensuring that projects contribute positively to the community. Ethical considerations, such as transparency, fairness, and respect for stakeholders, are also increasingly important.
Conclusion
The evolution of project management from the past to the present has been profound. Technological advancements have streamlined processes, improved communication, and enabled data-driven decision-making. Methodological shifts have introduced more flexible, adaptive approaches that prioritize continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Changes in team dynamics and the rise of remote work have necessitated new management styles and an increased focus on soft skills. Finally, the growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical considerations reflects a broader recognition of the impact of projects on society and the environment.
As project management continues to evolve, project managers must remain adaptable, continuously updating their skills and approaches to meet the changing needs of their organizations and stakeholders. The future of project management promises to be even more dynamic, with further technological innovations and shifting societal expectations shaping the way projects are managed and delivered. Nimble can help you stay ahead of these changes with its cutting-edge project management capabilities. It supports continuous learning and adaptability, enabling you to manage projects efficiently in an ever-evolving landscape. Ready to future-proof your project management approach? Sign up for a free trial of Nimble today!