What is a RACI Chart? A Complete Guide for Project Managers
- 8 mins read
-
By Linsa Saji
- Updated on September 26, 2024
In project management, maintaining clarity on roles and responsibilities is critical to ensuring project success. As teams grow more complex and project structures become more layered, confusion about who is doing what can lead to delays, miscommunication, and bottlenecks. This is where the RACI chart comes into play, serving as a vital tool for clearly defining who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed for each task in a project.

The beauty of the RACI model lies in its simplicity and adaptability across different project types, from traditional Waterfall frameworks to Agile methodologies. It brings structure to a potentially chaotic environment by breaking down project roles into four distinct categories. This structure ensures that everyone knows their place, not just in theory but in execution, which is crucial for project teams that span multiple departments, geographic regions, or expertise levels. For project managers and PMOs, this chart becomes a blueprint for ensuring accountability and facilitating communication among all team members and stakeholders.
What many industry experts overlook when discussing the RACI chart is the subtle balance it introduces in project decision-making. Unlike some other role-defining methods that focus solely on execution, the RACI model integrates decision-making and consultation into the core of project management. It emphasizes the importance of stakeholder involvement (Consulted) and provides a platform for them to offer input at critical stages without overwhelming the decision-makers (Accountable) or the task executors (Responsible). This creates a unique dynamic where stakeholders can remain engaged without causing project delays—a nuance that is often underappreciated.
Moreover, one of the lesser-discussed strengths of the RACI chart is its ability to minimize “role creep”—a common issue where multiple individuals assume the same responsibility, leading to either redundancy or critical tasks slipping through the cracks. By clearly assigning one accountable individual per task, the RACI chart keeps projects lean and efficient while ensuring no task is left unowned.
RACI Definitions Explained
At its core, the RACI chart is built on four key roles: Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. Each of these roles serves a distinct purpose, and understanding their nuances is essential to leveraging the full potential of this model in project management.
Responsible refers to the individual or group tasked with completing the work. They are the ones executing the tasks and ensuring that deliverables are met. Multiple people can be responsible for a task, especially in larger projects, but clear communication is crucial to ensure coordination.
Accountable is the single person who takes ultimate ownership of the task. While others may be responsible for doing the work, the accountable person ensures it gets done. They have the final say on decisions related to the task and bear the responsibility if things go awry. It’s a best practice to have only one accountable person per task to avoid confusion and ensure clear leadership.
Consulted are the experts or stakeholders whose input is needed before a decision or task can be completed. Their role is critical in ensuring that the work aligns with broader goals or specialized knowledge. Over-involving consulted parties can delay progress, so it’s important to carefully select who should be consulted.
Informed includes those who need to be kept up-to-date on progress but do not directly contribute to the task. These could be team members, managers, or external stakeholders who need to be aware of outcomes without having a direct influence on decisions or execution.
By assigning these roles explicitly for every task, the RACI model helps avoid misunderstandings and miscommunications, allowing for more seamless execution. However, a critical question for project managers is: when should you use a RACI matrix?
When Should You Use a RACI Matrix?
A RACI matrix is best utilized in projects that involve multiple stakeholders, cross-functional teams, or complex workflows. When accountability and communication start to become murky, a RACI chart can bring much-needed structure. For instance, large-scale projects that span several departments often suffer from overlapping responsibilities, leading to task delays. In such cases, a RACI matrix can help clarify who is in charge of each aspect of the project, preventing issues like role duplication or neglected responsibilities.

In contrast, small, simple projects where roles are already clear or teams are tightly knit may not require the formality of a RACI chart. The key is recognizing when your project needs that extra layer of role clarity and accountability to ensure a smooth and efficient workflow.
Benefits of the RACI Model in Project Management
The RACI model provides several key benefits that help optimize project management, especially in complex, cross-functional environments. The first and most evident advantage is role clarity. In many projects, particularly those involving large teams or multiple departments, responsibilities can become blurred. The RACI chart prevents confusion by clearly defining who is responsible for what task, ensuring that all team members understand their specific roles. This transparency reduces the risk of tasks being neglected or duplicated, leading to more efficient project execution.
Another benefit is enhanced accountability. The RACI model assigns a single accountable person for each task, ensuring that there is always one person overseeing the completion and quality of the work. This ownership minimizes delays and encourages quicker decision-making since the accountable person has the authority to drive the task forward. Moreover, the inclusion of consulted and informed parties ensures that stakeholders who need to contribute their expertise or be kept in the loop are involved without overwhelming the process. Overall, the RACI model streamlines communication, making it easier to coordinate across teams and functions, particularly in projects with multiple moving parts.
How to Make a RACI Chart?
Creating a RACI chart involves a structured, step-by-step approach that can be applied to any project, regardless of size or complexity. The first step is to identify all project tasks. A comprehensive task list should be prepared, outlining every action required to complete the project. This ensures that no steps are overlooked when assigning roles.
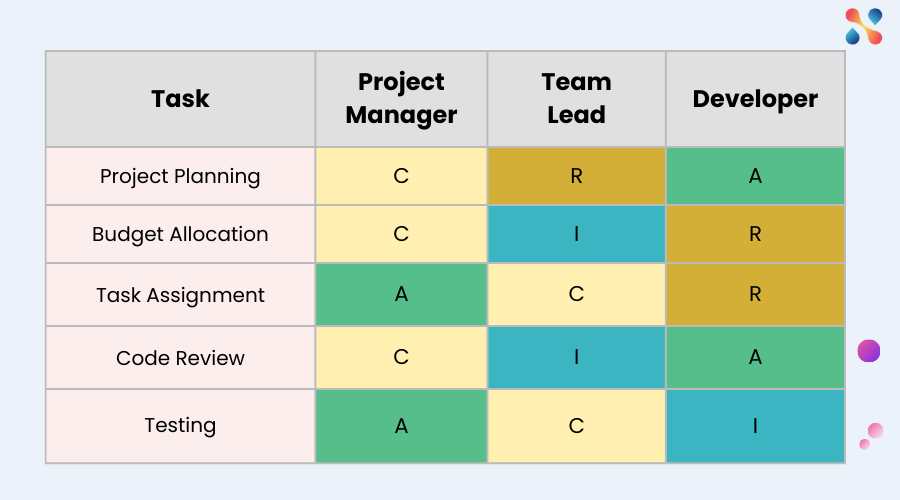
Next, assign the RACI roles to each task. Begin by determining who will be responsible for executing the work, followed by assigning who will be accountable for the task’s completion. It’s crucial to ensure that each task has only one accountable individual to avoid conflicts in decision-making. After that, identify the stakeholders who need to be consulted for their input and those who should be informed about the task’s progress.
Once roles are assigned, the chart should be reviewed for balance. Be mindful not to overload tasks with too many consulted or informed parties, as this can slow down decision-making. Finally, communicate the RACI chart with your team to ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities. Regular updates and revisions may be necessary as the project evolves, making the chart a living document that adapts to changes.
RACI Rules and Best Practices
To ensure the RACI chart functions effectively, certain rules and best practices should be followed. One of the most important rules is that each task should have only one accountable person. Multiple accountable people can lead to confusion and decision-making delays, as team members may hesitate to act if they believe others are also in charge. Clear, singular accountability is essential for maintaining progress.
Another best practice is to keep the chart simple. While it may be tempting to involve many consulted and informed individuals, over-complicating the chart can create unnecessary bureaucracy. Aim to limit consulted parties to those whose expertise is essential, and informed parties to those who need updates but don’t need to be involved in day-to-day decisions. Additionally, it’s important to regularly review and update the RACI chart throughout the project lifecycle. As the project evolves, roles may need to be reassigned, or tasks may change, making it crucial to keep the chart aligned with current realities. By following these guidelines, the RACI chart will remain a valuable tool for maintaining project clarity and efficiency.
When to Use or Skip a RACI Chart for Your Project
While the RACI model is a powerful tool for ensuring clarity and accountability, it’s not always necessary for every project. Knowing when to use or skip a RACI chart depends largely on the complexity and scale of your project. Use a RACI chart when your project involves multiple stakeholders, cross-functional teams, or high degrees of coordination. For example, large enterprise projects that span departments or geographical regions often suffer from communication gaps and unclear responsibilities. A RACI chart in these scenarios ensures that every task has an owner and that all key parties are involved appropriately, preventing bottlenecks and improving transparency.
On the other hand, smaller, simpler projects may not require the formality of a RACI chart. If roles and responsibilities are already clear, or if the project is being executed by a small, tightly-knit team, the added structure might slow things down rather than help. In such cases, more informal methods of communication and accountability can suffice. The key is to assess the complexity and communication needs of your project before deciding whether a RACI chart will add value or create unnecessary overhead.
Common RACI Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
While the RACI model can greatly improve project management, it’s not without its pitfalls. One common mistake is overloading the Consultant role, where too many stakeholders are asked for input. This can slow down decision-making and create unnecessary friction, as too many voices weigh in on every detail. To avoid this, limit the consulted parties to only those who are critical to the task at hand, ensuring swift and efficient progress.
Another frequent issue is unclear accountability. In some cases, project managers assign multiple accountable individuals to a task in an effort to distribute responsibility. However, this often leads to confusion, as no one feels truly responsible. To prevent this, ensure that each task has only one accountable person. Additionally, project teams sometimes fall into the trap of creating a RACI chart but failing to update it as the project evolves. Projects change over time, and roles may shift. Regularly revisiting and adjusting the RACI chart ensures it remains an effective tool throughout the project’s life cycle. By being mindful of these potential pitfalls, teams can use the RACI model to its full potential and avoid common challenges.
RACI Matrix Alternatives
While the RACI matrix is a popular tool for managing project roles, there are other alternatives that project managers may consider, depending on their needs. One such alternative is the DACI model, which stands for Driver, Approver, Contributor, and Informed. This model is more decision-focused, making it ideal for projects that involve significant decision-making processes. Another option is the RASCI model, which adds a Support role to the traditional RACI structure. This is particularly useful in projects where specific team members are tasked with providing assistance without being responsible for the final deliverable. Lastly, the MOCHA framework (Manager, Owner, Consulted, Helper, Approver) is another alternative that emphasizes leadership and ownership within projects.
However, despite these alternatives, the RACI model remains a staple in project management due to its simplicity and clarity. Its ability to clearly define roles and eliminate confusion makes it an invaluable tool for managing complex projects.
Bottom Line
Managing projects often involves navigating through complexity, miscommunication, and shifting responsibilities. The RACI chart offers a straightforward solution to these challenges by providing a clear framework for role definition. It ensures that team members know exactly who is responsible for execution, who is accountable for decisions, and who needs to be consulted or kept informed.
By mapping out responsibilities in a simple, easy-to-understand format, the RACI chart brings much-needed clarity to even the most complicated projects. It empowers project managers to keep workflows smooth, reduce delays, and avoid misunderstandings, enabling the team to stay focused on delivering results. While there are alternatives, the RACI model remains an effective tool for teams looking to improve coordination and accountability, ensuring that everyone stays aligned and the project stays on track.
Share the Knowledge
About Author:
Linsa Saji
Simplifying Project Management!
Explore Nimble! Take a FREE 30 Day Trial
PM 101
Marketing Metrics KPIs: The Ultimate Guide to Measuring Success
Unlock the power of marketing metrics and KPIs with this ultimate guide. Learn how to track, analyze, and optimize your campaigns for measurable success.
What is Digital Marketing? And Why is it Important for a Business?
Learn what digital marketing is and why it’s essential for businesses. Explore key strategies, benefits, and how it helps brands grow in the digital age.
How to Create a Digital Marketing Plan & Execute it with Nimble?
Learn how to create a digital marketing plan and execute it efficiently with Nimble. Discover strategies, tools, and best practices to drive marketing success.
How to Plan and Track Digital Marketing Campaigns?
Learn how to plan and track digital marketing campaigns effectively with key strategies, tools, and tips to ensure successful execution and measurable results.
Top 10 Tips for Social Media Management in 2025
Discover the top 10 tips for mastering social media management, including strategies for engagement, content creation, and staying ahead of evolving trends.
What is a Contingency Plan? 5 Steps to Create One
Learn what a contingency plan is and follow five key steps to create one for your project. Ensure your team is prepared to handle unexpected challenges and minimize risks.
What is a RACI Chart? A Complete Guide for Project Managers
Learn what a RACI chart is, how it clarifies roles and responsibilities in project management, and how to create one for your team to improve collaboration and accountability.
5 Best Templates for Product Development
Discover the 5 best templates for product development that streamline processes, enhance collaboration, and drive innovation. Optimize your product strategy with these top picks.



